Introduction to Waveguide Writing
In order to write waveguides, we simply focus a laser into a transparent sample, such as glass. This creates a local change in the glass that has different optical properties (index of refraction) compared to the glass around it. When we then move the glass or the laser beam, we trace a path which becomes an optical “channel” or waveguide. This happens because the light (wave) is confined (guided) to the channel created by the path of the laser through the material (glass).
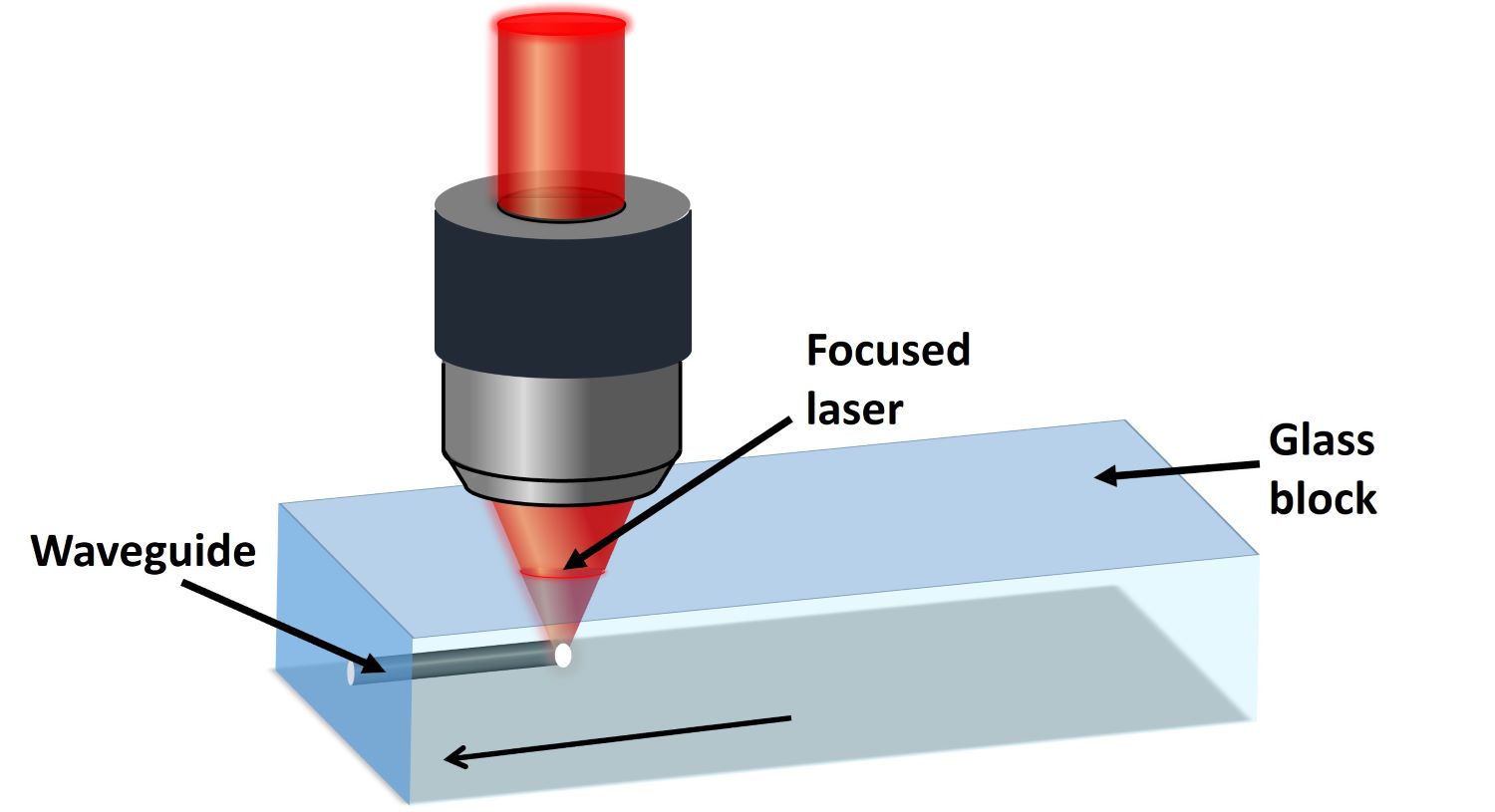
The focused laser beam moves through the glass block in the direction of the red arrow, tracing out the waveguide by changing the glass material as it goes.
Waveguide Writing Applications
In simple terms, waveguides can be used to move light from one place to another. They are not a one-size-fits-all solution and there are many ways to move light (e.g. via fibre, via ‘free-space’ i.e. sending the laser beam through air and others). Which method of transport the user chooses depends on the particular needs of the device or application they have, but in general, waveguides are often chosen when:
Overcoming The Space Constraints Of Fibres
A waveguide can be In the order of 10-20μm. While the core of a single mode fibre is ~9.5μm, the cladding on the fibre takes the size to 127μm or more. Waveguides can potentially be packed quite close together, but fibres are limited by the size of the cladding. The familiar example of this is in the area of chip-to-chip communication or transceiver applications, but other applications such as AR/VR/MR are emerging where space limitations are also driving the adoption of waveguides.
Efficient Compact Scale Connectivity
Since the glass connectors can be very small, propagation can be kept to a minimum. Waveguides written in glass suffer from relatively higher loss at 0.2dB/cm, while single mode fibres have losses of 0.2dB/km (note cm vs km!!)
Available on all devices
Capable of melee inscriptions
Suitable for coloured gemstones
High capacity (100k+ stones p/a)
Encryption secure IDs
Automation and machine vision
Remote service and diagnostics
Integrates with blockchain traceability solutions
Integrates with factory IM systems
Multiple stone loading
Available on all devices
Capable of melee inscriptions
Suitable for coloured gemstones
High capacity (100k+ stones p/a)
Encryption secure IDs
Automation and machine vision
Remote service and diagnostics
Integrates with blockchain traceability solutions
Integrates with factory IM systems
Multiple stone loading
“The ability to write waveguide circuits through laser processing is a key enabler for a wide range of technological applications. Opsydia’s technology will be central to creating versatile devices on the industrial scale.”

Prof. Martin Booth
Founder & Director, Opsydia
Latest News
Opsydia team visited Photonics West 2025
The Opsydia photonics leadership team attended the Photonics West conference and exhibition where one of our founding scientists, Prof. Patrick Salter presented a series of talks: Laser writing waveguides up to the sample edge Patrick S. Salter, Zhi Kai Pong, Martin...
Opsydia to Participate in the Pre-Loved Luxury Show in Paris
From November 15-17, 2024, Opsydia will take part in a unique event dedicated to the secondary market which encourages and advocates circularity, authentication and branding in the luxury goods economy. We are pleased to share more insights into this emerging...
Contact Us
To find out more about the Opsydia Systems or to discuss a trial or demonstration, please speak to a member of our team.


